Understanding Stop-Out Level And Its Role In Forex
Suppose you’re trading the EUR/USD pair with a leverage of 1:100, opening a position worth $100,000 with a mere $1,000 from your account. Suddenly, a market downturn decreases your equity, leading your broker to initiate a ‘margin call.’ Unable to meet this requirement, you experience the automatic stop-out process, resulting in the liquidation of your positions.
This is the reality of a stop-out level in Forex trading, a crucial mechanism that can drastically impact your trading journey and finances.
So, what is a stop-out level, why does it happen, and how can you avoid it?
What Does the Forex Stop-Out Level Mean?
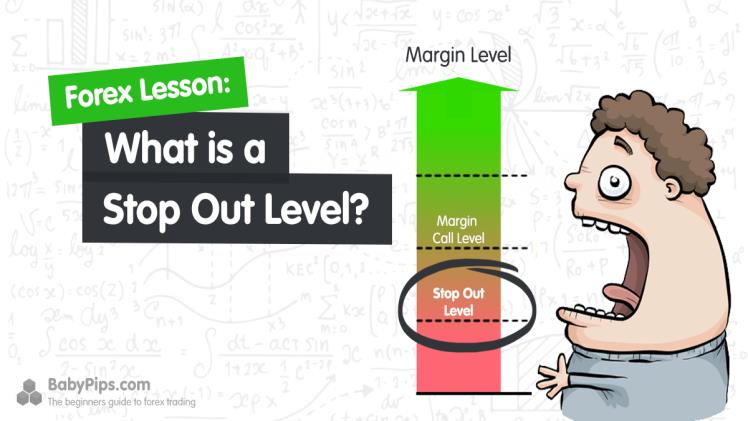
The stop-out level refers to the automatic closure of a trader’s positions when the account balance reaches a predetermined level. This concept is particularly relevant in the context of leverage in margin trading and can affect different traders in various ways.
Margin trading possesses the potential to amplify traders’ profits. However, it also carries considerable risk. Two frequently occurring market events associated with margin trading are stop-outs and margin calls, both of which can result in significant losses.
A trader maintaining multiple open positions, some at a loss, often witnesses a decrease in account balance. When trading with leverage, traders are required to meet a minimum margin requirement. If this requirement is not fulfilled, the broker initiates a process known as a margin call, urging the trader to deposit additional funds to recover the minimum margin and preserve the open position. If the trader fails to comply promptly, the broker starts liquidating the positions.
Notably, a margin call allows the broker to wait for additional funds from the trader instead of immediately selling off the client’s assets.
The situation could escalate if the trader does not promptly add more funds to their account. Each broker has a specific threshold for achieving the margin before the stop-out is automatically triggered. Once this point is reached, there’s no turning back – stop-out will activate, and all open positions will be closed until the margin level is reinstated.
Example of Stop-Out Level In FX Trading
Let’s consider a practical example to comprehend better the concept of stop-out in Forex trading. Suppose you’re using leverage of 1:20 to trade the EUR/USD currency pair. For a position of 100,000 euros, your required equity contribution is 5,000 euros. Your broker triggers a margin call if your equity falls to 2,500 euros—equivalent to 50% of your utilized margin.
You can infuse additional funds into your account or liquidate part of your assets in response to a margin call. If neither is undertaken, the broker has the right to sell off your assets independently, and stop-out will activate.
Some brokers might opt to wait, allowing traders to make the decision. While this approach might seem beneficial, it can backfire if market trends continue to counter your positions, leading to further losses.
Methods for Determining the Stop-Out Level
Usually, it is unnecessary to determine the stop-out level independently. Most brokers on the market today will take care of this for you. However, understanding a stop-out and how to calculate it is still beneficial. stop-out is essentially a percentage-expressed required margin level.
One method for determining the stop-out level is by using specialized calculators. Forex traders must enter data for the account currency, equity, currency pair, buy/sell price, and volume position in lots into the stop-out level calculator.
The calculator then generates information such as the current price, the distance to the stop-out level, the stop-out price, and the potential losses associated with your positions. Using these tools can help traders anticipate worst-case scenarios.
Even though the stop-out level varies from broker to broker, it’s commonly set around 20%.
Tips for Preventing Stop-Out in Forex
Now that we know what a stop-out level in forex is let’s find out how to avoid it. Many traders are terrified of stop-outs given their potential for significant losses. Consequently, it’s only logical to search for strategies that can help mitigate the risk of encountering a stop-out.
Ensuring you have a solid risk management strategy is the most straightforward approach to avoid stopping out. This can be accomplished by using intelligent orders, such as stop losses, which traders use to set specified levels to liquidate positions if the market moves against their trade automatically. This strategy helps prevent traders from incurring losses beyond their risk tolerance.
Making sure you don’t have a lot of positions open at once is another strategy to prevent dealing with stop-out levels. With each open order, more equity is utilized, thereby increasing the risk of your account nearing the stop-out level.
Another crucial step you can take to prevent dealing with a Forex stop-out is to make sure you respond to margin calls promptly and accurately. You should know that failing to answer the margin call could result in a stop-out, meaning losing all your positions.
Conclusion
Overall, stop-out can carry great risk, so individual traders must be prepared for adverse market conditions and a scenario that could quickly turn against them. The risks are significantly greater if you don’t have a well-developed risk management strategy.





