What is an Order Book in Trading
With the trading industry rapidly growing, competition and standards are also rising. As a result, several important aspects must be considered when trading, including market tracking, security, and transparency.
Fortunately, solutions are also increasing in parallel to provide a better overall experience. One standout solution is the order book, which can be an excellent tool for analyzing price trends and markets.
This blog post explores the fundamentals of an order book and highlights its role in trading.
Fundamentals Of Order Book
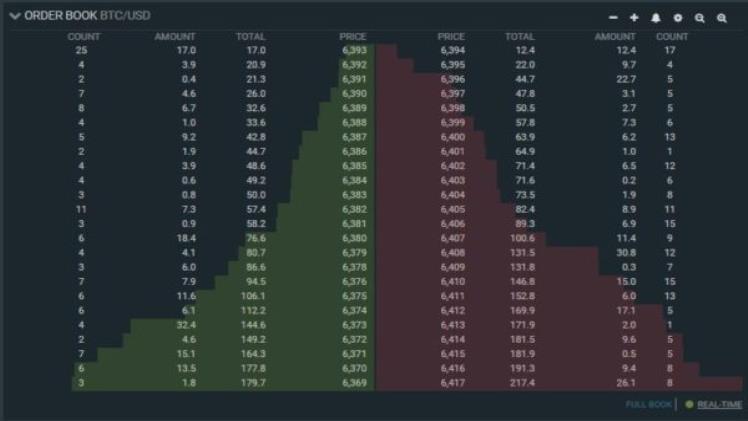
An order book serves as a digital ledger that maintains and organizes purchase and sale requests for a particular financial asset, sorted by their respective price levels.
The quantity of shares on bid or offer at every price level, also referred to as the market depth, is shown for each level in the order book. It also identifies the market participants behind these orders, though some prefer to remain anonymous. Such lists prove to be crucial for traders, as they contribute to improved market transparency by delivering important trading information.
Exchanges use to organize and display orders for various assets, such as stocks, bonds, and cryptocurrencies like BTC. These orders can be submitted manually or electronically.
While the information provided is generally the same, the layout and presentation may vary depending on the source. Buy and sell information may be located at different positions on the screen, either at the top and bottom or on the left and right sides.
Order books are constantly updated in real-time throughout the day, making them dynamic. Nasdaq, for example, refers to this as the “continuous book.” However, orders specifically for execution at market open or market close are kept separate. These are known as the “opening book” and “closing book” respectively.
To determine the opening and closing prices, the opening book and continuous book are combined at the Nasdaq market open, and the closing book and continuous book are consolidated at the market close. This consolidation process generates a single opening price and a single closing price.
What Does ‘Reading An Order Book’ Mean?
The order book consists of three essential parts: buy orders, sell orders, and order history.
Buy orders include bids and the desired quantity, while sell orders include offers or asking prices for those willing to sell. The order history displays all past transactions.
At the top of the book, you’ll find the highest bid and lowest ask prices, indicating the prevailing market and the necessary price for executing an order. Additionally, a candlestick chart is commonly found alongside the book, offering valuable insights into the current and past market conditions.
The order book is a valuable tool for traders to make more informed decisions. It allows them to see which brokerages are actively buying or selling stocks, giving them insight into whether retail investors or institutions drive market activity.
Additionally, the order book displays order imbalances that can offer clues about the short-term direction of a stock.
Understanding the Diverse Structures
In financial trading, different types of orders are used to buy or sell assets at specific conditions. The four common order types are: market order, limit order, stop-loss order, and trailing stop. Each order serves a distinct purpose and offers unique features to traders.
Understanding these order types through an example can help investors make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively in the market.
- A market order allows you to instantly buy or sell a financial instrument at the current market price. For instance, if a share of Apple (AAPL) is currently priced at $300, placing a buy order at this price will result in the purchase of the share for $300.
- A stop-loss order functions similarly to a limit order. When your stock price falls to a predetermined level, the trading platform automatically sells your shares, closing out your position. This feature effectively prevents further losses.
- A trailing stop is a mechanism that determines the selling price of your shares by a specified percentage below the market price. It follows the market price if it increases but remains at the lower specified amount if it drops. This allows you to secure higher profits and limit potential losses.
- A limit order is a specific type that allows you to buy or sell a financial instrument at a predetermined price. The trading platform or exchange automates this process. You can place a limit order at that price. The trade will only be executed if the shares can be purchased at $298.50 or lower, ensuring you buy or sell at your desired price. Essentially, a limit order sets a strict price limit for trading.
Aspects To Consider
The order book is designed to provide transparency in the market, but it doesn’t include all the details. One such detail is the existence of “dark pools,” which are hidden orders maintained by large players who want to keep their trading intentions private.
Dark pools play an important role in preventing significant price devaluation on exchanges. When information about a large institution’s big transaction becomes public before the trade is executed, it usually causes the security price to drop. However, if the information is reported after the transaction, it may impact the market less.
Dark pools diminish the usefulness of the order book to some extent because we can’t determine if the orders shown truly reflect the supply and demand for the stock.
Bottom Line
To effectively gauge interest in a tradable instrument, it is crucial to comprehend the workings of order books. Examining an order book gives you a comprehensive understanding of market depth.
Additionally, familiarizing yourself with different types of orders and their functions is key to becoming a responsible and thriving trader. Initially developed for the stock market, these techniques are now equally relevant in the crypto industry.