Complete Guide to Rotator Cuff Repair from Your Trusted Orthopaedic Clinic in Singapore

The shoulder is one of the most flexible and frequently used joints in the body, allowing you to lift, rotate, and reach with ease. Maintaining shoulder health and function is essential for daily activities, sports, and overall quality of life. At the center of shoulder movement is the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that stabilise the shoulder joint and enable smooth motion. However, rotator cuff injuries are common, especially among athletes, older adults, and those performing repetitive overhead movements. When these injuries occur, they can cause pain, weakness, and limited mobility, often affecting everyday tasks.
This article serves as a complete guide to rotator cuff repair, covering everything from diagnosis and treatment options to surgical procedures and recovery, helping patients understand what to expect and how to regain shoulder function. For more detailed information about rotator cuff repair and how our orthopaedic clinic can help, read more here https://www.artisanorthopaedics.sg/surgery/rotator-cuff-repair.
What is a Rotator Cuff Injury?
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that work together to stabilise the shoulder joint and enable smooth movement. These muscles allow you to lift, rotate, and perform overhead activities with ease. A rotator cuff injury occurs when one or more of these tendons or muscles are damaged, leading to pain, weakness, and reduced shoulder mobility.
Rotator cuff injuries are common and can affect people of all ages. In younger adults, they are often caused by sports-related activities, such as swimming, tennis, or weightlifting, where repetitive overhead motions place stress on the shoulder. In older adults, degenerative changes in the tendons over time can lead to tears, even with minor movements. Other risk factors include previous shoulder injuries, poor posture, and repetitive manual work.
Symptoms of a rotator cuff injury can vary depending on the severity of the damage. Common signs include persistent shoulder pain, difficulty lifting the arm, weakness when performing daily activities, and sometimes a clicking or popping sensation. Left untreated, these injuries can worsen over time, potentially leading to chronic pain and limited function.
When is Rotator Cuff Repair Needed?
Not all rotator cuff injuries require surgery. Many mild tears or strains can be managed with non-surgical treatments such as physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and activity modification. Rotator cuff repair is usually considered when conservative treatments fail to relieve pain or restore function, or when the injury involves a complete tear that significantly affects shoulder strength and mobility.
Certain signs may indicate that rotator cuff repair is necessary:
- Persistent shoulder pain, especially at night or during overhead activities
- Weakness when lifting or rotating the arm
- Loss of range of motion
- Difficulty performing daily tasks, such as dressing or reaching for objects
An orthopaedic specialist will evaluate the severity of the tear through a physical examination and imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Prompt assessment and timely repair can prevent further damage and improve the chances of a successful recovery, restoring shoulder strength and function.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis is crucial before deciding on rotator cuff repair. At an orthopaedic clinic, specialists use a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests to evaluate the shoulder and determine the extent of the injury.
The assessment typically includes:
- Medical history review: Understanding how the injury occurred, symptoms, and any previous shoulder issues
- Physical examination: Checking shoulder strength, range of motion, and identifying areas of tenderness or weakness
- Imaging tests:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of muscles, tendons, and ligaments
- Ultrasound: Helps visualise tendon tears and assess their severity
- X-rays: Sometimes used to rule out bone problems or arthritis
Why diagnosis matters:
- Confirms the type and severity of the rotator cuff injury
- Helps the orthopaedic specialist determine whether non-surgical treatment or rotator cuff repair is needed
- Guides the selection of the most suitable surgical technique if repair is necessary
- Ensures a personalised treatment plan for optimal recovery
Rotator Cuff Repair Procedures
There are several surgical approaches to repairing a torn rotator cuff, depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Common procedures include:
- Arthroscopic repair: Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a camera to guide the repair
- Open repair: Traditional surgery involving a larger incision to directly access the tendon
- Mini-open repair: Combines arthroscopy and a small incision for tendon repair
What to expect during surgery:
- Tendons are reattached to the bone
- Any frayed tissue is trimmed or smoothed
- The approach is chosen based on tear size, patient age, and overall shoulder condition
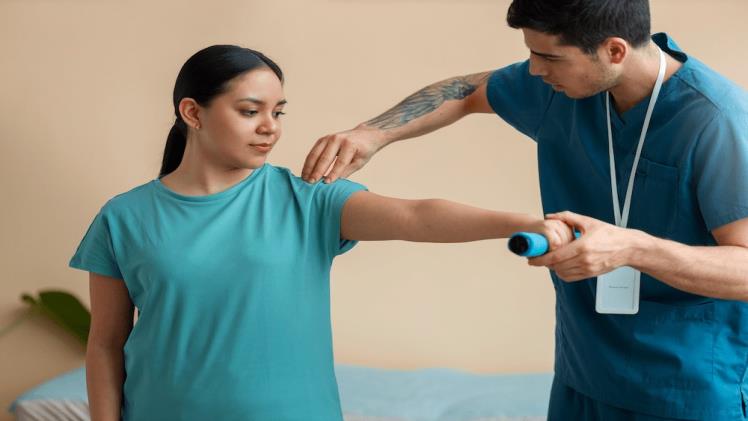
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after rotator cuff repair involves several stages to ensure proper healing and restore shoulder function. Patients typically start with a period of immobilisation using a sling to protect the repaired tendon. Gradually, gentle exercises are introduced to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness.
Key rehabilitation points:
- Physiotherapy sessions tailored to the injury and surgery type
- Gradual increase in range-of-motion exercises
- Strengthening exercises once the tendon has sufficiently healed
- Avoidance of heavy lifting or overhead activities until cleared by the specialist
- Regular follow-ups to monitor progress and adjust therapy
Risks, Benefits, and Expected Outcomes
Understanding the potential risks and benefits of rotator cuff repair helps patients make informed decisions and set realistic expectations.
Potential risks include:
- Infection at the surgical site
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
- Re-tear of the tendon
- Pain or discomfort during recovery
Expected benefits:
- Reduced shoulder pain
- Improved strength and stability
- Restored range of motion
- Enhanced ability to perform daily activities and sports
Overall outcomes:
- Most patients experience significant improvement with proper rehabilitation
- Recovery may take several months, but long-term function and quality of life are often greatly improved
Conclusion
Rotator cuff injuries can affect shoulder function, but timely assessment and treatment can restore mobility and reduce pain. For expert evaluation and personalised care, consult the specialists at:
Artisan Sports & Orthopaedic Surgery – Hip & Knee | Shoulder & Elbow | Shockwave Therapy Singapore
290 Orchard Road, Paragon Medical Centre #07-12, Singapore 238859
Phone: +65 8909 8877